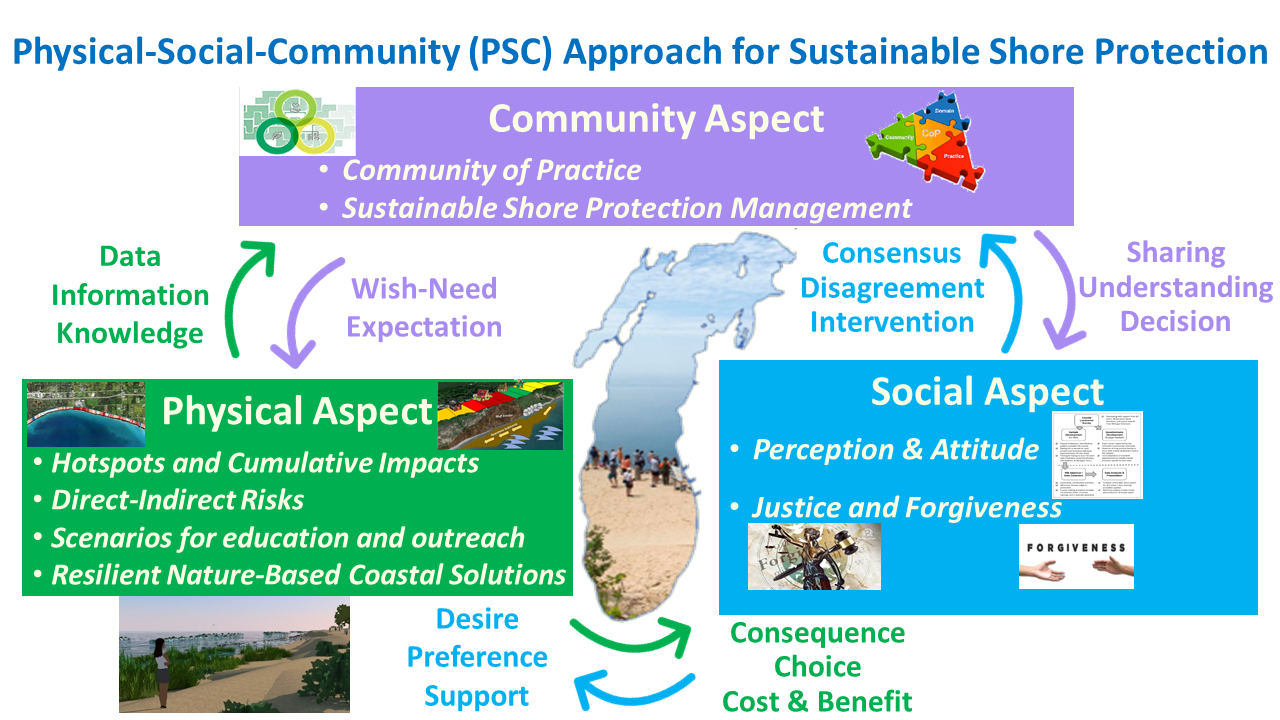
An Integrated Physical-Social-Community (PSC) Approach for Sustainable Shore Protection, Beach Integrity, and Bluff/Dune Stabilization Along Lake Michigan
Private landowners, communities and public officials along the Lake Michigan coast face many challenges - climate and weather hazards, shore and beach erosion, bluff and dune recession, and failing coastal protection structures - and protecting one property can cause problems for adjacent properties. In addition, complex human-coastal environment interactions and human-human interactions combined with coastal shore protection options often prompt conflict among stakeholders. Previously, there have been no readily available techniques to resolve these conflicts. This project will work to improve resilience in coastal cummunities on the Lake Michigan coast through a science-based, integrated Physical-Social-Community (PSC) approach thath helps to build sustainable shore rotection, understand attitudes and perceptions related to behavior change or adoption of shore protection options, employ Just and Forgiving Community to enhance community social resilience and establish multi-way communications within and between coastal communities for all of Lake Michigan.
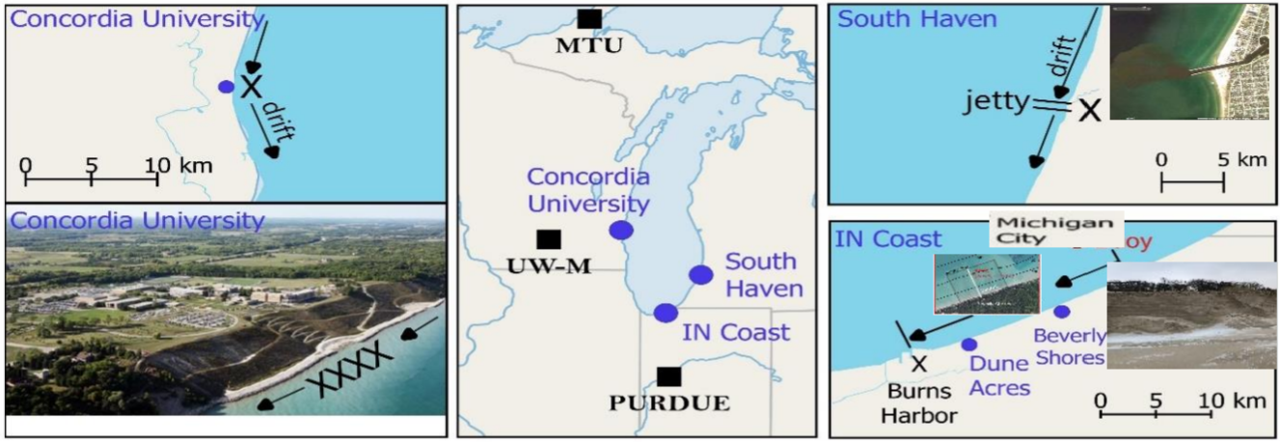
COastal Sediment Transport Assessment for Resilience and Sustainability (COSTARS)
OBJECTIVE
- Address coastal erosion, accelerated bluff failure, and beach disappearance amid high water levels, intensifying storms, and ongoing coastal development
- Characterize bluff stability and beach integrity
- Develop sustainable shore protection sholutions by modeling the coatsal hydrodynamics and morphodynamics under changing climate scenarios


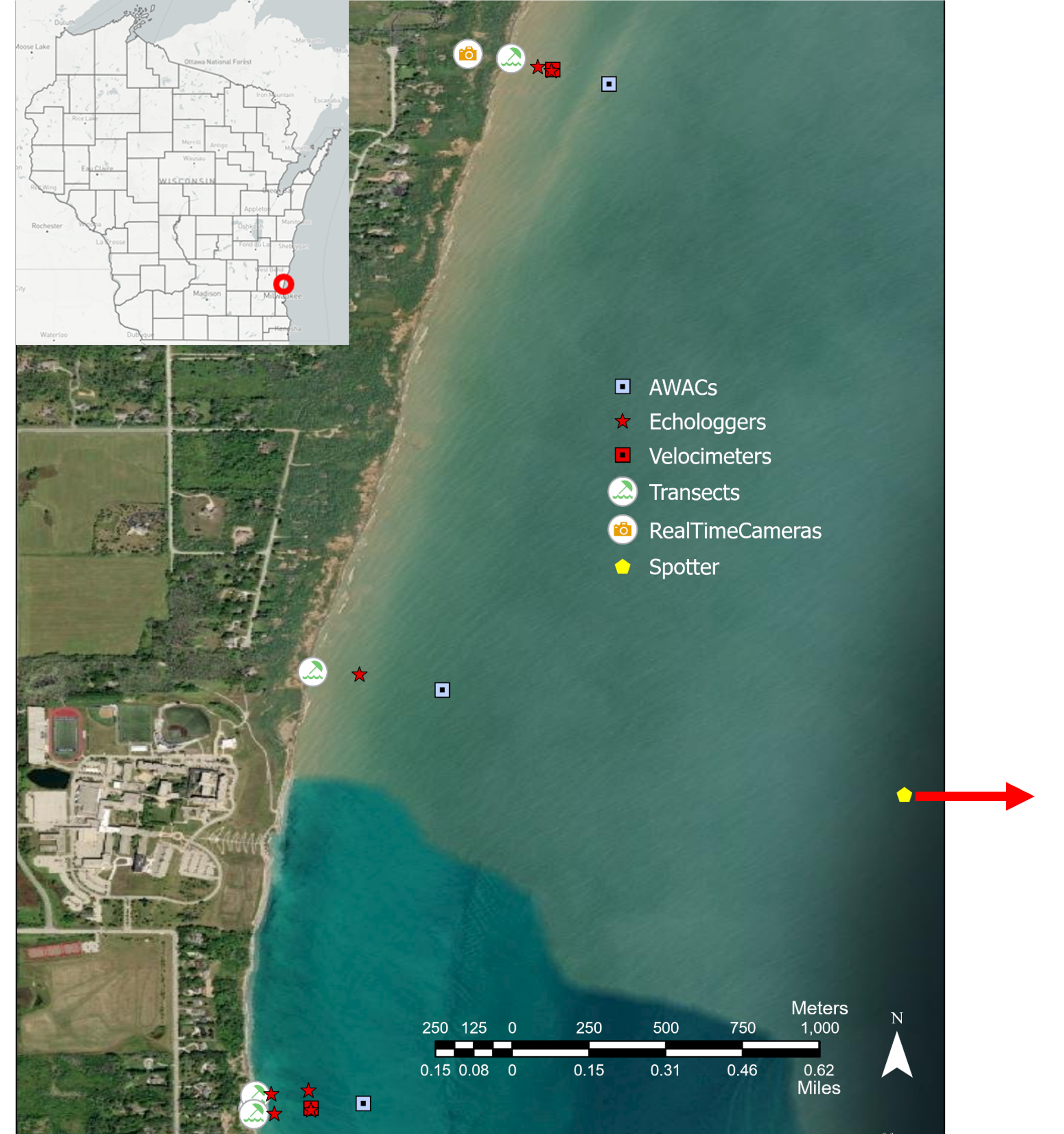
WISCONSIN INSTRUMENT LOCATIONS